Exact knowledge of the current groundwater levels, and hence also of the groundwater resources, is crucial for the State of Berlin, since the water for the public water supply of Berlin (233 million m³ in the year 2019) is provided from groundwater. The groundwater is pumped at nine waterworks, almost entirely within the city area, with the exception of the waterworks Stolpe. It is located on the northern outskirts of the city and pumps water from wells that are located in Brandenburg (approx. 9 % of the total annual pumping volume) (Fig. 1).
Groundwater Levels of the Main Aquifer and Panke Valley Aquifer 2020
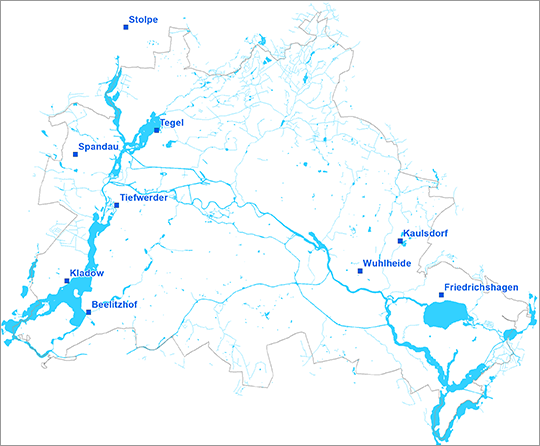
Fig. 1: Location of the waterworks which supply Berlin with drinking water, as of May 2020
Image: Umweltatlas Berlin
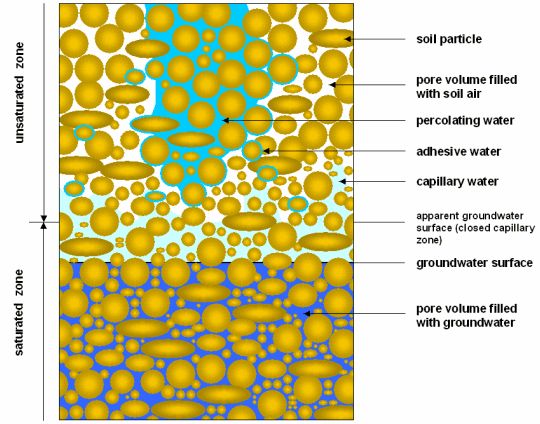
Fig. 2: Types of appearance of subsurface water
Image: modified after Hölting 1996
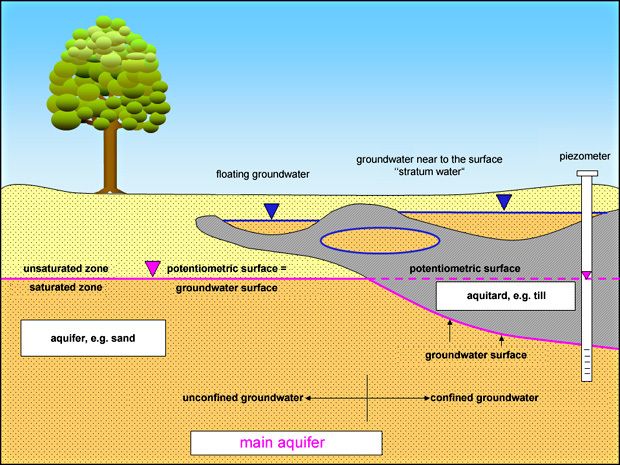
Fig. 3: Hydrogeological terms
Image: Umweltatlas Berlin
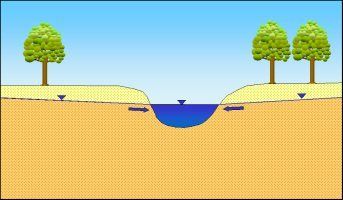
Fig. 4a: Groundwater infiltrates into the surface waters (effluent conditions)
Image: Umweltatlas Berlin
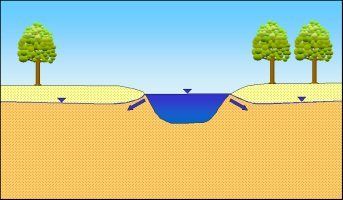
Fig. 4b: Bank-filtered water caused by flooding: Surface water infiltrates into the groundwater (influent conditions)
Image: Umweltatlas Berlin
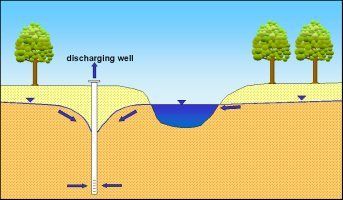
Fig. 4c: Bank-filtered water caused by discharge of groundwater: due to the drop in the groundwater caused by wells, surface water infiltrates into the groundwater
Image: Umweltatlas Berlin
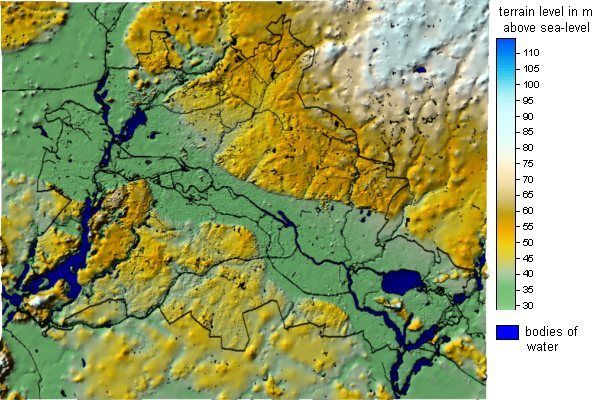
Fig. 5: Morphological map of Berlin
Image: Umweltatlas Berlin
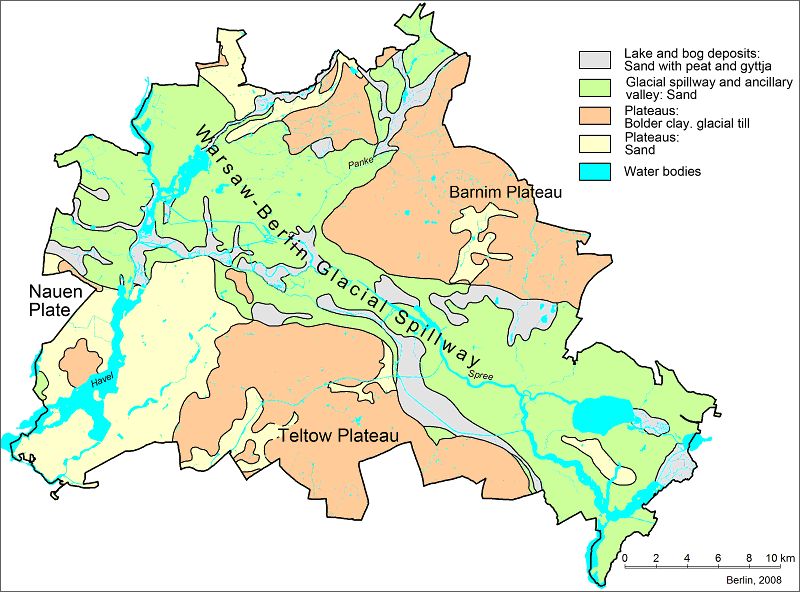
Fig. 6: Geological map of Berlin
Image: Umweltatlas Berlin
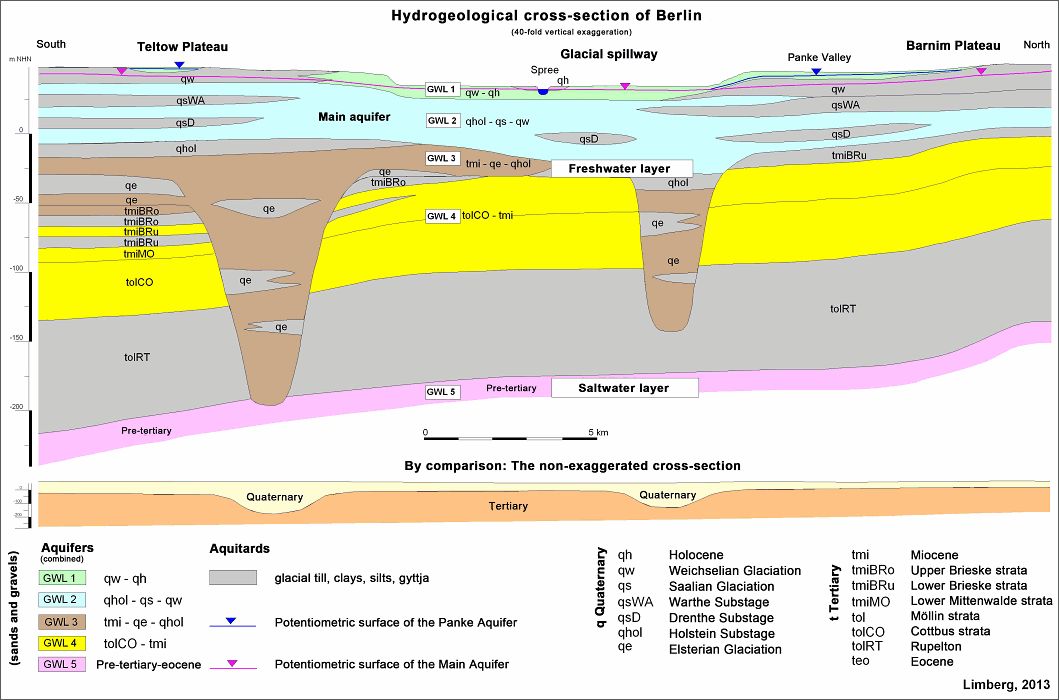
Fig. 7: Schematic hydrogeological cross-section of Berlin, from south to north
Image: from Limberg, 2013
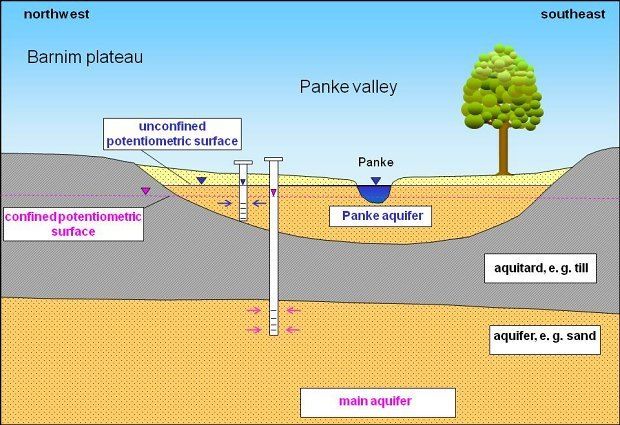
Fig. 8: The unconfined Panke Valley Aquifer (Aquifer 1) in the north-western area of the Barnim Plateau is situated above the Main Aquifer (Aquifer 2), which is confined in this area
Image: Umweltatlas Berlin
