Long-term Development of Selected Climate Parameters 2013
Berlin-Tegel
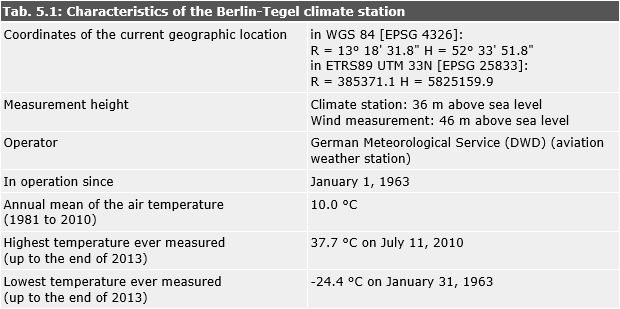
Tab. 5.1: Characteristics of the Berlin-Tegel climate station
Image: Umweltatlas Berlin

Photo 5.1: Location of the Berlin-Tegel aviation weather station (see arrow mark)
Image: SenStadtUm 2014
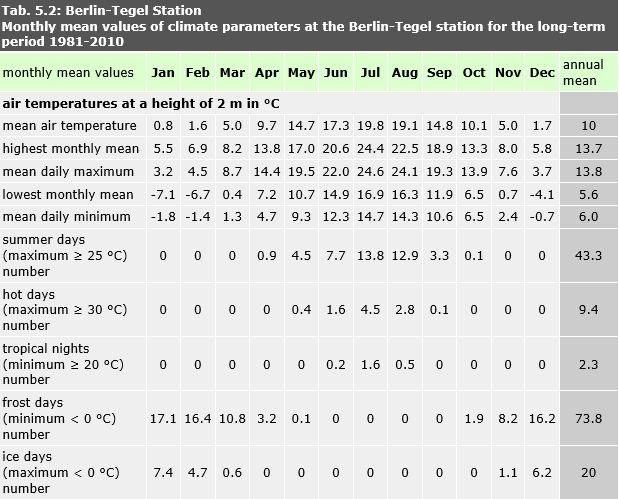
Tab. 5.2: Monthly mean values of climate parameters at the Berlin-Tegel station for the long-term period 1981-2010
Image: statistical base DWD, processing GEO-NET 2014
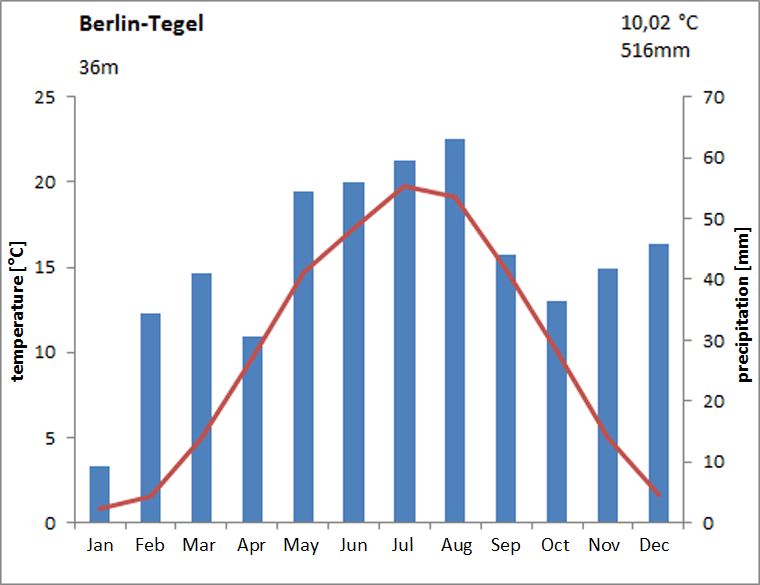
Fig. 5.1: Climate diagram for the Berlin-Tegel station for the long-term period 1981 to 2010
Image: GEO-NET 2014, Knerr 2014
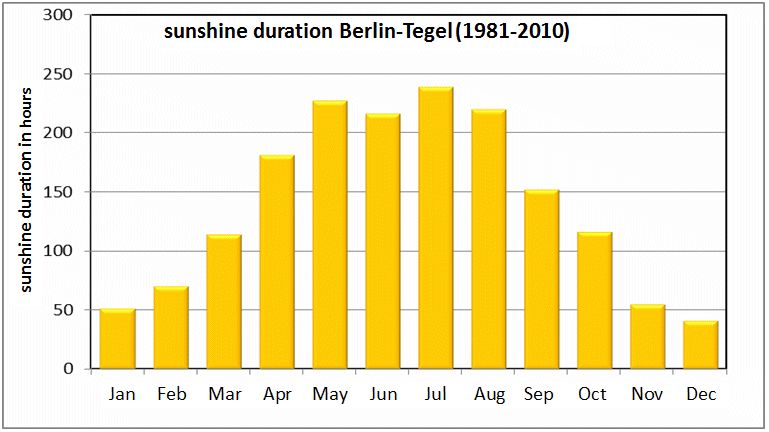
Fig. 5.2: Mean monthly sunshine duration at the Berlin-Tegel climate station for the long-term period 1981 to 2010
Image: statistical base DWD, processing GEO-NET 2014
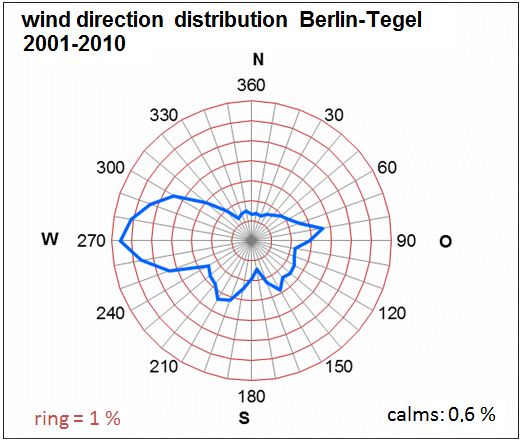
Fig. 5.3: Mean wind direction distribution in the period 2001 to 2010 at the Berlin-Tegel aviation weather station (measurement height 10 m). The ring lines indicate the frequencies of occurrence of the wind directions, their distance corresponds to 1 %
Image: statistical base DWD, processing GEO-NET 2014
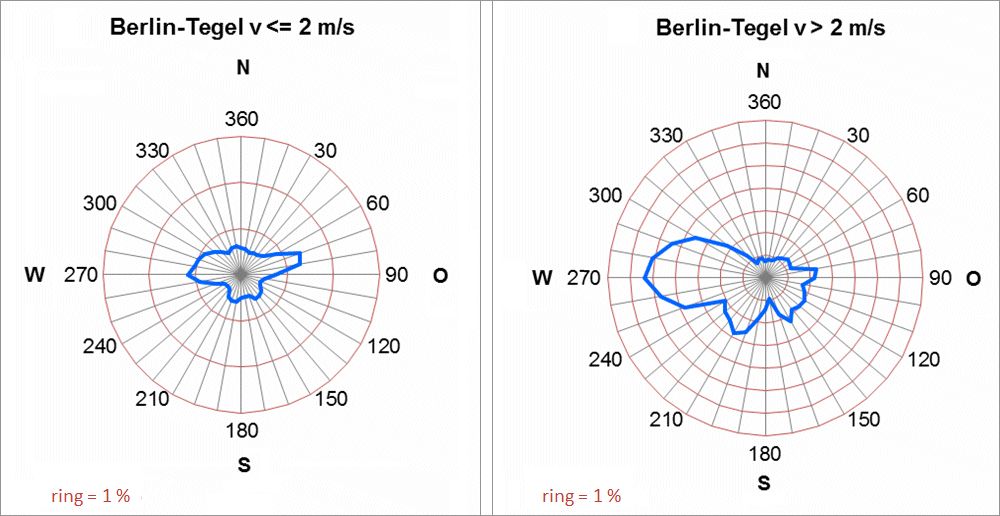
Fig. 5.4: Frequencies of the wind directions in the annual mean in the period 2001 to 2010 at the Berlin-Tegel aviation weather station by wind speed
Image: statistical base DWD, processing GEO-NET 2014
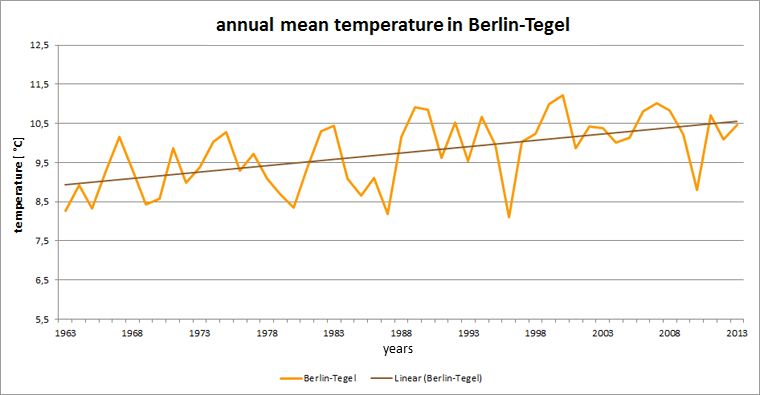
Fig. 5.5: History of the annual mean temperature at the Berlin-Tegel station in the measurement period 1963 to 2013
Image: GEO-NET 2014, Knerr 2014
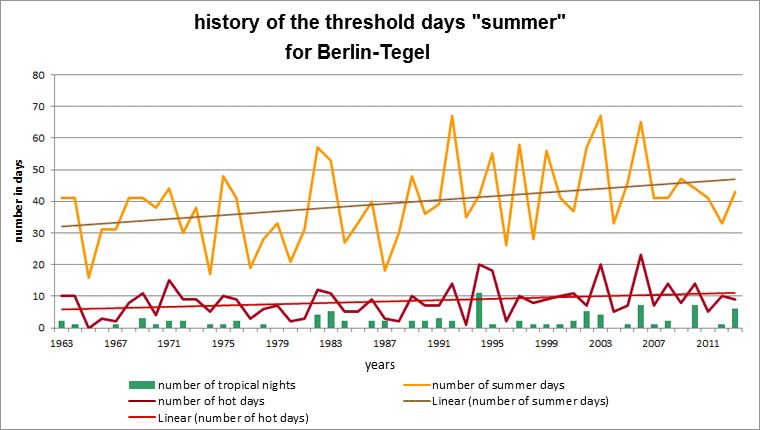
Fig. 5.6: History of the threshold days summer day, hot day and tropical night at the Berlin-Tegel station in the measurement period 1963 to 2013
Image: GEO-NET 2014, Knerr 2014
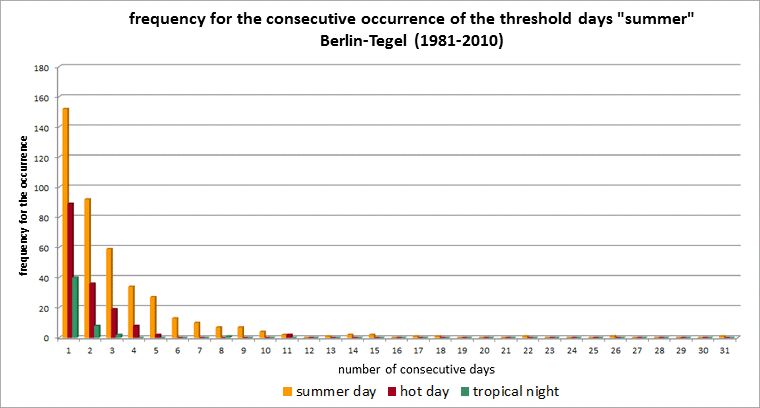
Fig. 5.7: Frequency of occurrence of consecutive summer days, hot days and tropical nights for the long-term period 1981 to 2010 at the Berlin-Tegel station
Image: GEO-NET 2014, Knerr 2014
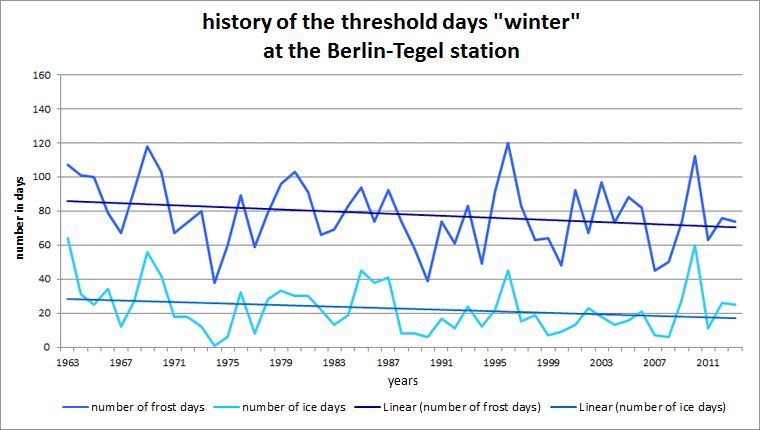
Fig. 5.8: History of the threshold days frost day and ice day at the Berlin-Tegel station in the measurement period 1963 to 2013
Image: GEO-NET 2014, Knerr 2014
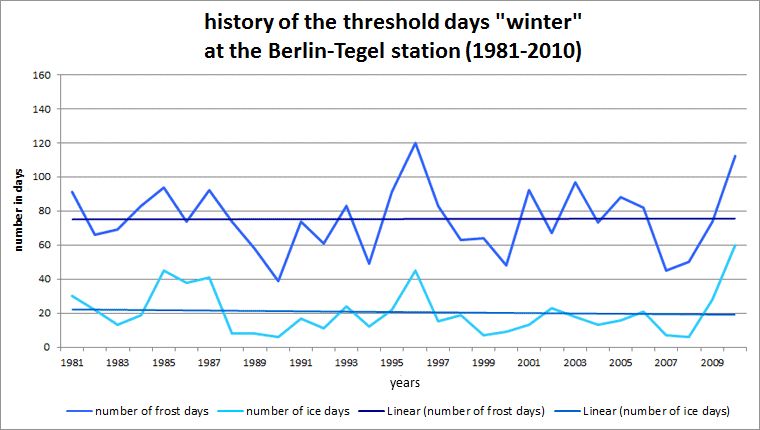
Fig. 5.9: History of the threshold days frost day and ice day at the Berlin-Tegel station for the long-term period 1981 to 2010
Image: GEO-NET 2014, Knerr 2014
