The category Forest includes all wooded areas which appear clearly in aerial photography as forest stands. Besides the wooded areas of the Berlin forests, this includes reforested former sewage farms and other areas with forest-like vegetation.
Not included in this category are forest-like parks, such as parts of the Großer Tiergarten or the Volkspark Klein-Glienicke, which is part of the parkland inventory of Berlin. Such areas have been assigned to the use category Park / green space and to the area type Forest.
Body of water includes all natural bodies of water, e.g. rivers, lakes, and also canals, retaining and seepage basins of the Berlin Water Authority (BWB), provided they are recognisable as water surfaces (or as water engineering structures).
The category Meadow and pasture includes meadows, pastures and enclosures used for agricultural purposes, and also experimental areas used by the universities for similar purposes, and former sewage fields, regardless of how the products of these fields are used.
Farmland includes areas identified as being used for agricultural purposes. It differs from the category Meadow and pasture in that the farmland is periodically ploughed, sown, fertilised and harvested.
To determine the use of Meadow and pasture and Farmland, the database of the digital field block register was analysed. The use categories Meadow and pasture and Farmland may alternate over the course of only a few years in the same area. For these two agricultural use categories, it is therefore particularly important that the mapping process reflect the current state of knowledge.
The category Tree nursery / horticulture includes both the acreage of private tree nurseries and garden centers, and of borough garden centers and city horticultural schools. These are areas with predominantly outdoor cultivation. Facilities with purely indoor operations are rather assigned to the category Commercial and industrial use.
Block areas with borough garden centres, horticultural schools, the work yards of the horticultural offices, and certain research facilities, such as the Institute for Crop Research of the Humboldt University Berlin, but also experimental areas of federal institutes such as the Federal Biological Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry (BBA), are mapped as dual use together with Public use / special use. Due to their high demand for space, tree nurseries and horticultural facilities are largely located on the outskirts of the city.
In addition to those facilities listed in the Green-Space Information System (GRIS) (SenUVK 2020) maintained by the Senate Department, the category Park / green space includes other green spaces, if they are similar in appearance to a publicly accessible park facility and are apparently subject to regular maintenance gardening. Thus, for example, well maintained green spaces associated with traffic areas along roads and motorways are assigned to this category, albeit as dual purpose areas with traffic use. Smaller, public-square-like green spaces and playgrounds are also mapped as a Park / green space, provided they are less than approx. one third impervious; otherwise they fall under the category of City square / promenade. Blocks of the use category Park / green space are also generally assigned to the area type Park / green space. Very extensive parks and
recreational facilities characterised almost exclusively by extensively maintained or non-maintained wooded or meadow-like areas are in some cases assigned to the area types Forest or Fallow area (e.g., the Volkspark Klein-Glienicke). Some special facilities that may not be accessed for free, such as the Botanical Gardens or Zoologischer Garten or Tierpark Friedrichsfelde, are mapped as a Park / green space, but with the dual purpose assignment as Public use / special use. Other public facilities, too, may be associated with green facilities. These parklands are then not delimited separately, even if their size exceeds the ascertainment limit of one hectare. They may be mapped as dual purpose areas, in order to also connote their predominantly “green” character.
By contrast however, private outdoor facilities, playgrounds, etc. in residential areas are not mapped as a Park / green space, since they are part of the character of the residential use of those areas, and the open space structure of these blocks is further differentiated in the area type assignment (see comments on the Environmental Atlas Maps “Urban Structure” (06.07) and “Urban Structure – Area Types Differentiated” (06.08)).
City squares / promenades are the public spaces of urban living. City squares serve as places of sojourn for leisure and recreational purposes, as meeting areas, market places etc., and are often located in front of railway stations and other representative public buildings.
Promenades are spacious pathways that provide pedestrians and cyclists with space for movement away from road traffic. Promenades may also include some more highly impervious median strips, provided they are not used as parking lots. Squares and promenades generally have a higher degree of imperviousness than parks and green spaces.
A Cemetery includes both areas currently used for burial purposes and former cemeteries, provided they are still recognisable as such.
The data on the inventory of cemeteries in Berlin (SenStadtWohn 2017, only in German), available from the appropriate Senate Department, forms the basis for the scope of these areas. Memorials, such as the Soviet War Memorial at the edge of the Großer Tiergarten, on the other hand, are not assigned to the area type Cemetery, although they are recorded in the Berlin inventory of cemeteries; they are mapped as Public and special use, and assigned to the area type Culture.
However, cemeteries are not generally considered areas of Public and special use. Only when usually small-scale blocks are largely occupied by a church building, and the surrounding cemetery is only a subordinate feature will a dual use as Public and special use be assigned, in which case the block is then assigned to the area type Church. However, if a church or chapel is located on a large cemetery only in a subordinate function, no dual use is assigned.
Structurally, cemeteries differ from one another mainly in terms of their stock of trees. While older park cemeteries and forest cemeteries are essentially characterised by their very old stocks of trees, many newer cemeteries are still largely without larger trees.
For the category Allotment garden, the data base on Berlin’s Allotment Gardens (SenStadtWohn 2020d) maintained by the appropriate Senate Department forms the basis for the classification and delimitation of the same. It records the allotment gardens with appropriate use, as defined by the Federal Allotment Garden Law.
Other areas with similar use characteristics are classified as Weekend cottages and allotment-garden-type use.
A Fallow area is an area that is not in use or maintained at the time of recording, on which variegated stands of vegetation can often develop undisturbed, which is, however, subject to great pressure of use and change.
A distinction is made between a Fallow area free of vegetation on the one hand, which includes mostly excavations, soil or rubble dumps, or demolition areas, where no vegetation has yet taken root, due to the fact that their utilisation has only recently been abandoned. In some cases, the site conditions ensure that no vegetation will enter the area for some time. These may be brownfields where little vegetation grows due to the very high degree of imperviousness, or else sand dunes and beaches, on which spontaneous growth of vegetation occurs only very slowly, due to a lack of nutrients, or due to regular disturbances.
Another category of fallows is Fallow area with predominantly meadow-like vegetation. On open brownfield sites, a vegetation of ruderal perennials and grasses often establishes itself during the first few years. Especially on nutrient-poor sites, this vegetation can remain relatively constant over the course of several years. In general, however, unstable conditions prevail.
All fallow areas which cannot be clearly assigned to one of the other fallow or forest categories are mapped as Fallow area with mixed vegetation – meadows, trees, bushes. The development of vegetation on a fallow site depends on many conditions, such as the abiotic site conditions, the initial vegetation and anthropogenic influences, so that on long-fallow sites, various successional stages often alternate within a small area.
If, on the other hand, an area is covered almost entirely with trees, it will be assigned to the category Forest.
The category Sports use includes both covered and uncovered sports facilities. All sports use areas are at the same time mapped as Public and special use.
Uncovered sports facilities are outdoor facilities used for sports, physical activity and leisure activities. These include not only sports fields, outdoor swimming pools and beaches, but also riding, golfing, archery and water sports areas. The latter are characterised by small dockyards, boat and club houses, parking lots etc., with a high proportion of green space. Clearly commercial water sports areas (dockyards, boat-building facilities, etc.) are assigned to the category Commercial and industrial use. Some fairly extensively used beaches (without changing rooms, kiosks, etc.) are assigned to fallow or forest categories.
Covered sports facilities include primarily those housed in halls, such as indoor pools and ice skating rinks, and also stadiums and multipurpose halls, in which non-sporting events such as concerts may also be held.
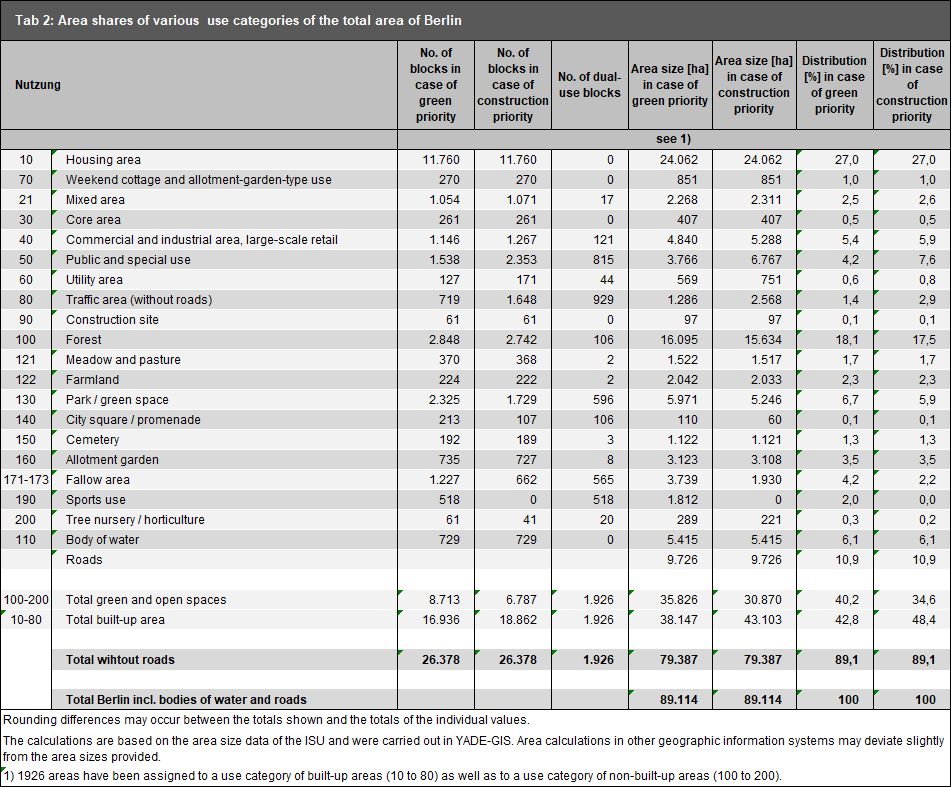
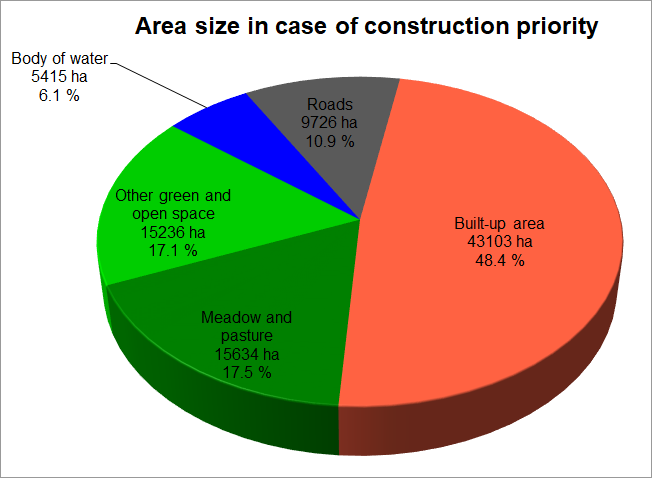
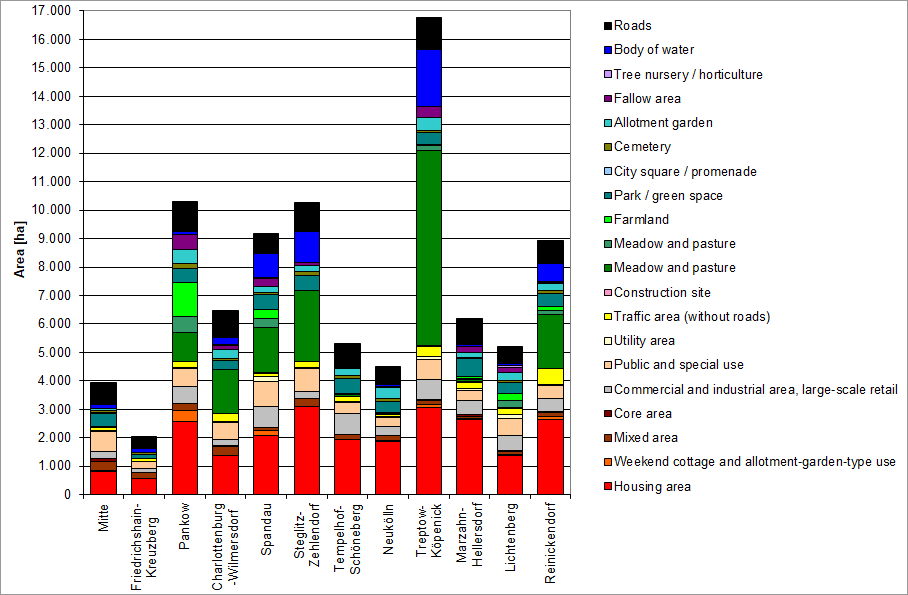
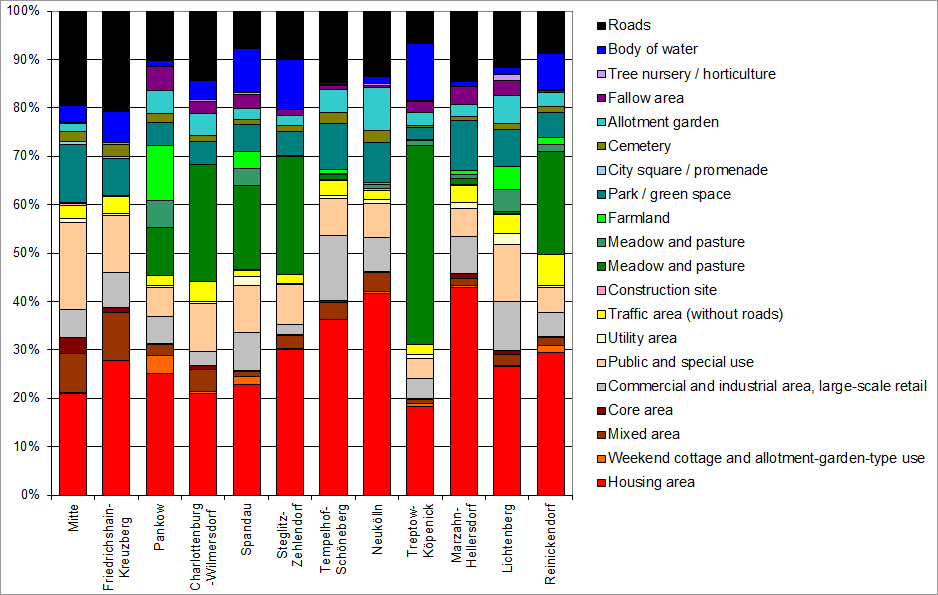

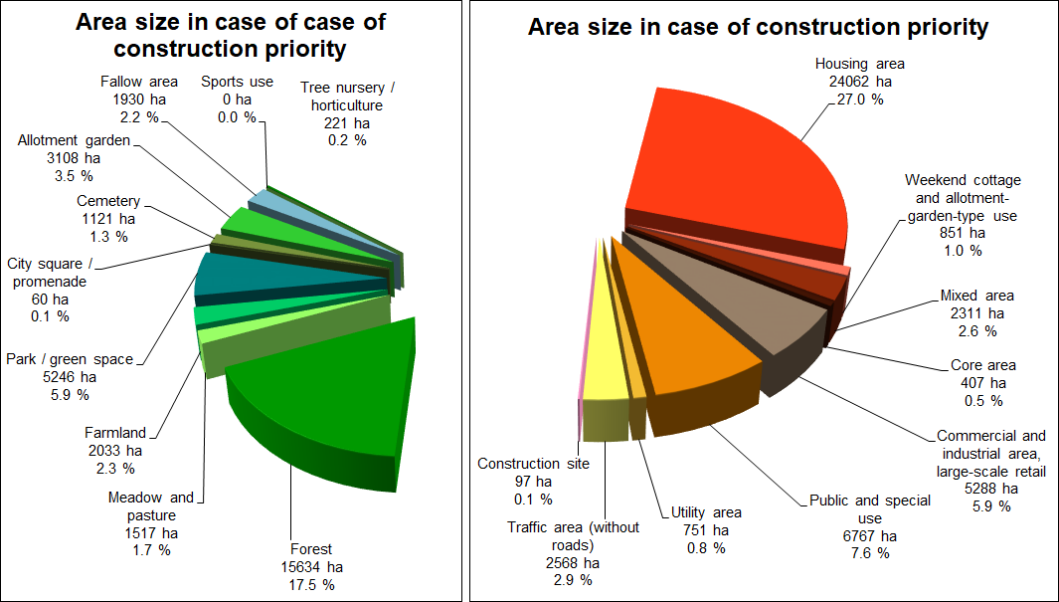
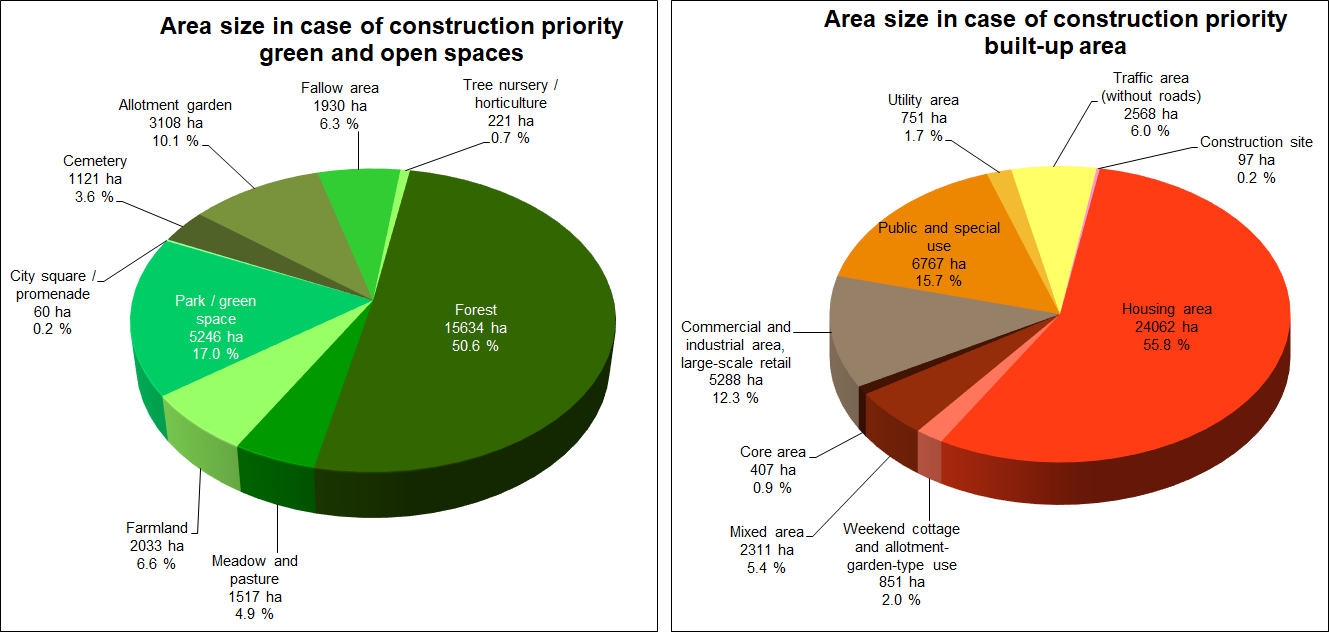
![Enlarge photo: Tab. 3: Area shares of various use categories of the total area of Berlin [in ha], area sizes based on the ISU5 block (segment) area map (in case of construction priority), as of December 31, 2020](/imgscaler/6gMliGrfSgE-8aIQT_rhQldwDzk9bz3Xhg2_d2aFyfs/ropen/L3N5czExLXByb2QvdW13ZWx0YXRsYXMvX2Fzc2V0cy9udXR6dW5nL2ZsYWVjaGVubnV0enVuZy9lbi10YWJlbGxlbi9ldDYwMV8wM18yMDIwX2dpZi5naWY.jpg?ts=1681470319)