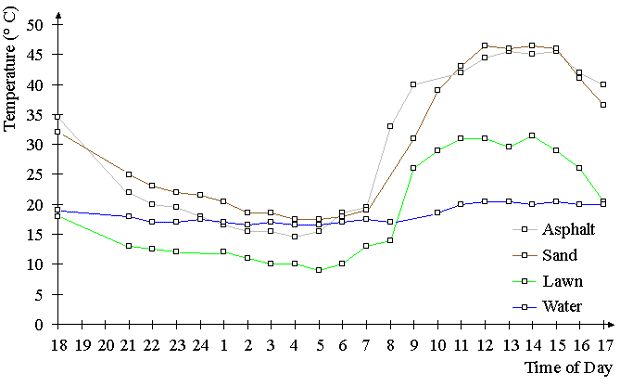
At the same time, the relative atmospheric humidity too is reduced, since vegetation-covered areas and the evaporation they generate is lacking. This can lead to the occurrence of extreme values which can impair human well-being considerably. In this context, pervious areas, such as parks, play a major role. Parks of even one hectare in size or more have a demonstrably positive climatic effects on human well-being. Vegetation-covered areas also have an effect on the dust and pollutant contents of the air, since, with their large leaf surfaces, they are able to bind dust particles and other air pollutants.
The effects of impervious coverage on the Berlin urban climate are described in detail in various maps of the chapter Climate.
Impervious coverage of the soil also causes profound changes in the water balance, due to the loss of evaporation and seepage surfaces for precipitation. The rainwater runoff from impervious areas, heavily polluted by tire abrasion, dust, dog excrement, etc., is passed by via the sewage system either directly into the tributaries or into sewage-treatment plants (cf. Map 02.09, Management of Rain and Waste Water).
Impervious coverage and condensation moreover strongly disturb the functions of the soil. The blockage of the water and oxygen supply destroys most soil organisms. Since no more water can seep down, the pollutants introduced via the air and precipitation are no longer retained in the soil, and are washed into the surface waters.
The complete impervious coverage of the soil causes the complete loss of all flora and fauna, but even partial impervious coverage always means habitat loss. Biotopes are fragmented or isolated, while sensitive species are crowded out in favour of more adaptable species.
In addition to the above-described consequences for the ecosystem, the degree of impervious coverage in urban areas also has an immediate effect on the human habitat. A high degree of impervious coverage is usually associated with a disparity of open space per capita. Long rows of buildings, frequently interrupted only by asphalt or concrete surfaces, can have a depressing, monotonous effect on residents. Such factors of nature as the change of the seasons can no longer be experienced in the immediate residential environment. Increased dependence on nearby recreation areas at the outskirts of a city on the other hand generates traffic, which also has a negative effect on the environment.
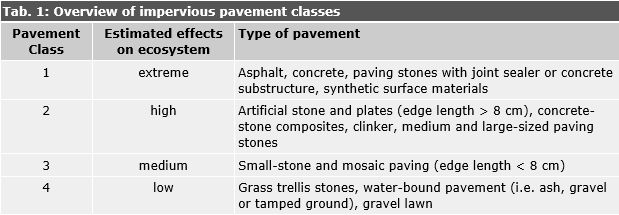
Impervious Coverage and Land Consumption in Germany
In Germany, impervious areas accounted for approx. 6 % of the total area in 2010. This corresponds to an impervious area of 2.16 million ha (State statistical offices, 2011).
In the political debate, the environmental indicator “land consumption” is primarily cited, and has also found its way into the national sustainability strategy.
There, since 2002, the goal of reducing land consumption to 30 ha per day by 2020 has been formulated. Daily land-consumption demand in Germany for residential/commercial and traffic use was 78 ha in 2009 (UBA 2011). Nationwide, the increase in areas used for buildings and open spaces is clearly on the decline. The increase in land areas used for traffic purposes, while it is lower than the increase in areas used for residential/commercial purposes, is still approx. 23 ha/day, and has thus not changed over the course of the past 20 years. Land consumption has been reduced in recent years, due to the economic situation, the drop in new road building, and the impervious coverage regulations for new buildings; however, it is still a long way from the target for 2020.
Land consumption is calculated from the daily increase in built-up and traffic areas. This is not equal to the impervious area, since it also includes areas which are only slightly impervious, such as gardens in residential areas or green median strips on roads, etc.
The Federal-State Cooperative Association for Soil Protection (LABO) in 2005 appointed a group of federal and state experts to develop a suitable assessment procedure for ascertaining soil impervious coverage at the state level, in order to expand the sustainability indicator “land consumption for residential/commercial and traffic areas” to include the component impervious coverage.
The results of the experts’ group are incorporated into the System of Integrated Environmental and Economic Accounting (SEEA) by the Working Group on Environmental-Economic Accounting of the German States (EEAL), and have been documented in the report Indikator Versiegelung, (the indicator “Impervious Coverage”/ Frie & Hensel 2007). See too the Excursus Versiegelungsdaten [impervious coverage data] 2011 and 2005, below, which compares the present results with those of the Indikator Versiegelung, by the EEAL.
The reduction of land consumption, which is a goal of the Sustainability Strategy, is to be achieved by space-reduced construction of buildings, densification of urban areas, concentration of infrastructure, provision of compensation areas, and the removal of impervious surfaces no longer used (space recycling). With the increase of the quality of the living environment in residential areas, concentrated housing in the city is to be reestablished as an alternative to the “home in the green suburbs” once again. (Bundesregierung 2007). Germany’s states and municipalities are to realize these targets in the context of their spatial and construction planning.
Legally mandatory stipulations are also being used to reduce impervious coverage. The impervious-coverage removal requirement under §5 of the Federal Soil Protection Law (BBodSchG) of 1998 is designed to provide compensation for land consumption, by causing areas no longer used to be made pervious again, and thus regain their natural soil functions, as per §2 Sect. 2 BBodSchG. The law makes allowance for reasonable expense and burden (Oerder 1999, .pp. 90 ff.). However, since costs and reasonableness of the imposition are taking into account, this regulation has not proven itself in practice.
A further possible instrument for reducing impervious coverage is financial incentives at the individual level. For example, Berlin has since January 1, 2000, invoiced the charge for precipitate-water sewage separately. The introduction of this so-called fee-splitting is based on a ruling by the Federal Administrative Court (ruling of June 12, 1972) and the Superior Administrative Court of Lüneburg (rulings of June 14, 1968 and of April 10, 1980). These rulings stated that in municipalities in which the cost of precipitate-water sewage disposal accounts for more than 15% of the total costs of sewage disposal, the fees must be invoiced separately, so that the fee for precipitate-water sewage disposal is no longer linked proportionally to the general sewage fee, but is rather charged according to the impervious share of the property from which waste water is fed into the sewage system (BWB 1998). Therefore, owners have since 2000 endeavoured to
keep the impervious area of their property as low as possible, in order to save on sewage fees. Since the new Precipitate-Water Exemption Ordinance of August 2001 came into effect (the Ordinance on Exemption from Requirement for Permission for Harmless Percolation of Precipitate Water – NWFreiV, August 24, 2001), it is possible to obtain proportionate or full exemption from the precipitate-water sewage disposal fee (SenStadt 2001) via measures for relieving the rainwater sewage system via-water percolation on one’s own property, without permission.